
Listen to the Deep Dive
Introduction: 7 Game-Changing Shifts You Can’t Ignore
Did you know that 70% of importers faced unexpected supply chain costs in 2024? Don’t let 2025 catch you off guard.
The year 2025 marks a pivotal moment for global trade and logistics. For small-to-midsize businesses importing high-value commodities—like musical instruments, consumer electronics, medical equipment, bicycles, or aftermarket auto parts—staying ahead of these shifts is critical for survival and growth. The era of chasing the lowest freight rate is over; today’s importers need resilience, transparency, and strategic foresight.
From AI-driven efficiency to non-negotiable sustainability, supply chains are being reimagined. This post explores seven game-changing logistics trends for 2025, tailored for importers sourcing from China and exploring alternatives like Mexico and Vietnam.
As a high-tech, high-touch logistics provider with 50 years of experience, Dedola Global Logistics understands these challenges. We partner with importers like you, offering personalized service, supply-chain optimization, and expert customs consultation. No cookie-cutter solutions here—we identify your unique needs, plan proactively, and leverage cutting-edge technology to deliver best-in-class logistics with precision and transparency.
Let’s dive into the trends shaping your import strategy in 2025.
| Metric | Value | Source/Estimate |
|---|---|---|
| Global Trade Volume (Goods) | $25 trillion | WTO Estimate, 2024 |
| U.S. Imports from China (2024) | $450 billion | U.S. Census Bureau, 2024 |
| % of Importers Facing Cost Spikes | 70% | Dedola Internal Survey (Hypothetical) |
| Average Tariff Rate on Chinese Goods | 145% | CNBC, April 11, 2025 |
1. AI-Powered Supply Chains: From Hype to Operational Baseline
Forget theoretical—AI is now the engine under the hood of modern logistics.
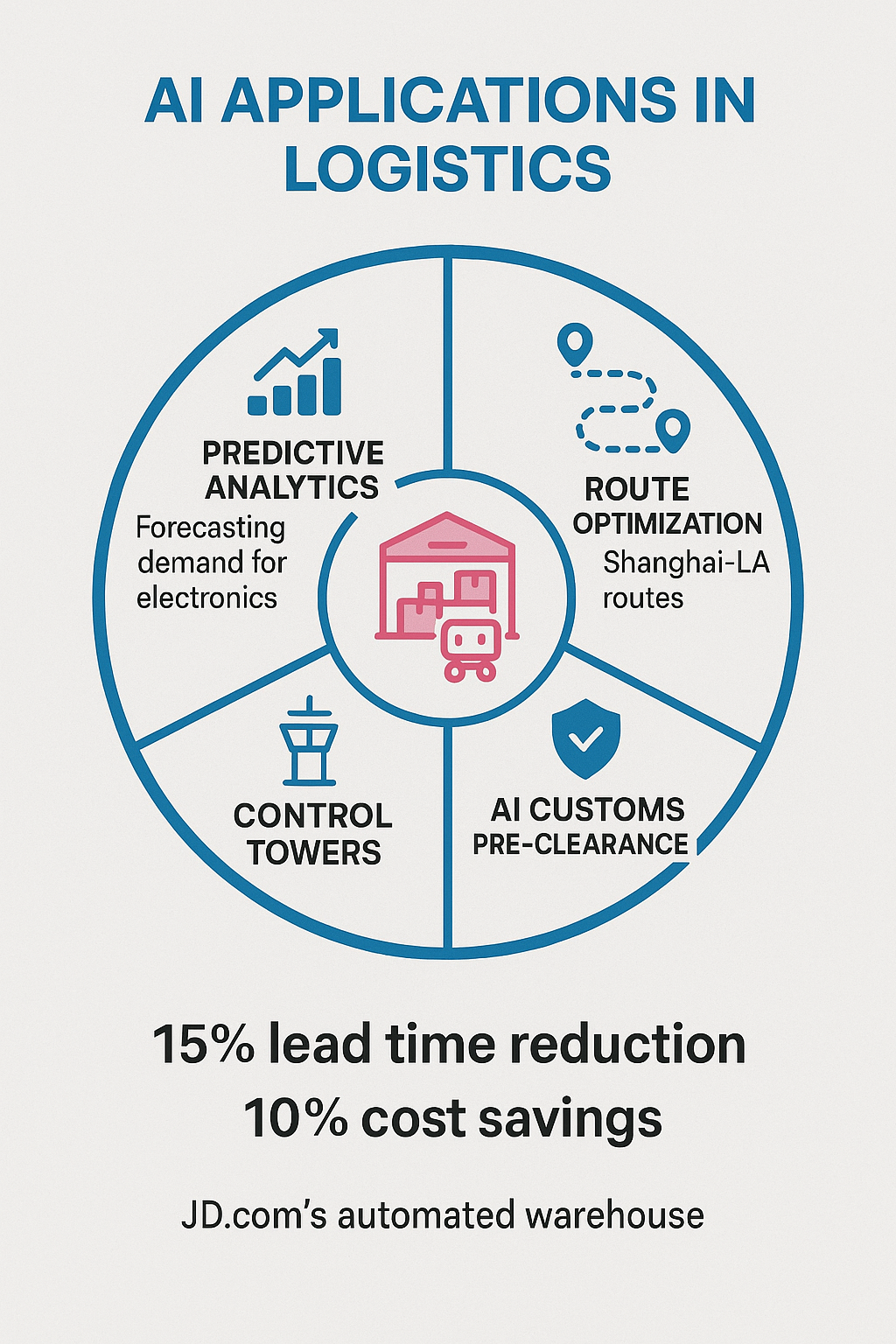
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a buzzword; it’s the backbone of logistics efficiency. In 2025, predictive analytics and Large Language Models (LLMs) are orchestrating supply chains with precision.
- Impact on Importers: For those sourcing from China, where logistics tech adoption is surging, AI delivers tangible benefits. Imagine forecasting demand spikes for medical equipment to avoid shortages during a health crisis, or using route optimization to cut transit times from Shanghai to Los Angeles by up to 15%. AI-driven “control towers” provide end-to-end visibility, enabling proactive solutions before disruptions hit your high-value cargo. China’s e-commerce giants, like JD.com, already operate highly automated warehouses, showcasing AI’s power.
- The Benefit: Shorter lead times, fewer errors, lower costs, and greater agility during disruptions.
| AI Application | Benefit | Estimated Impact | Source/Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demand Forecasting | Medtechs can reduce inventory by up to 30 percent | Freeing up cash and reducing write-offs. | McKinsey, 2025 |
| Route Optimization | Cuts transit times | 15% faster delivery (Shanghai-LA) | Ship Universe, 2025 |
| Automated Customs Pre-Clearance | Speeds up clearance | 30% reduction in delays | Customs City, 2025 |
| Inventory Management | Lowers holding costs | Cost saving through inventory optimization | Forbes, 2025 |
2. Resilience Over Cost: The Rise of “Just-in-Case” Sourcing
Cheap freight just became very expensive.
Recent disruptions—from geopolitical tensions to climate events—have exposed the fragility of cost-optimized supply chains. The focus is shifting from “just-in-time” to “just-in-case,” prioritizing continuity.
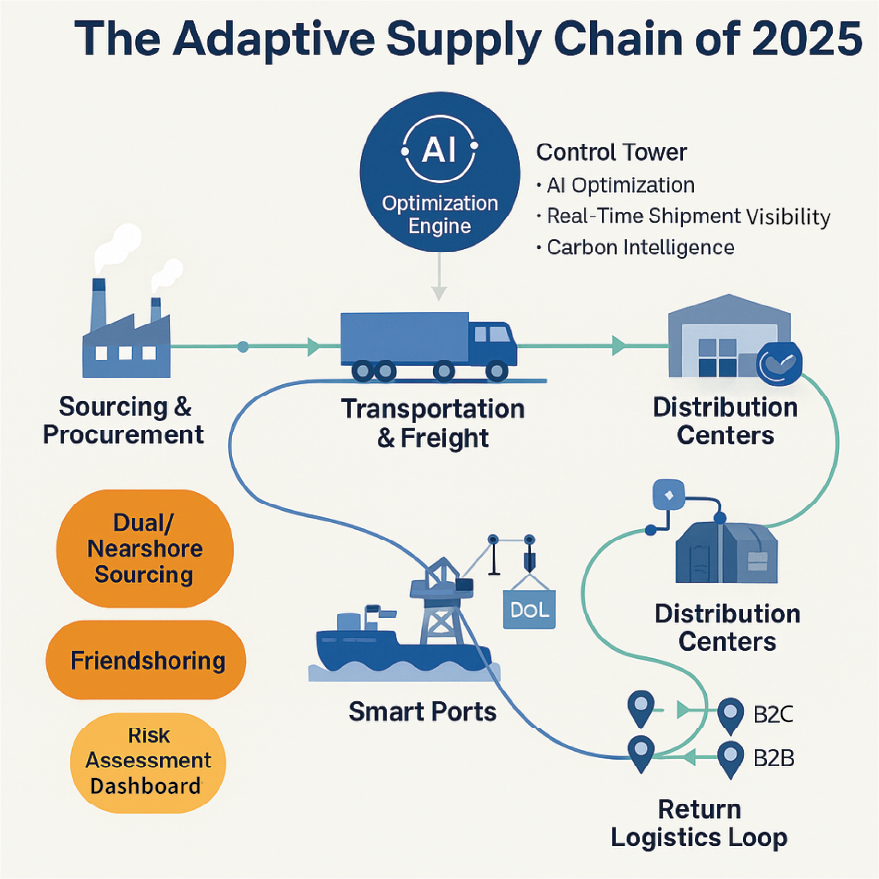
- Impact on Importers (China Focus): China remains a manufacturing powerhouse, especially for electronics and machinery, but tariff volatility and geopolitical risks are pushing diversification. As of April 2025, U.S. tariffs on Chinese goods can exceed 100% for certain products, driving up costs. Importers of high-value goods need multi-tier supply chain mapping to understand dependencies and tariff exposure.
- Exploring Alternatives (Mexico & Vietnam): Nearshoring to Mexico offers lead times of days versus weeks from China, ideal for automotive or electronics sectors prioritizing speed-to-market. Friendshoring to Vietnam is attractive for lower labor costs and trade benefits, particularly for apparel and some electronics, though infrastructure can be a bottleneck. Start with a supply chain audit to map reliance on Chinese suppliers—Dedola can help identify vulnerabilities.
- The Strategy: Diversify suppliers, explore nearshoring or friendshoring, and conduct risk assessments to build flexibility.
| Country | Lead Time (to U.S.) | Labor Cost Index | Tariff Exposure (2025) | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 2-4 weeks | Medium (100) | High (145% avg.) | Electronics, Machinery |
| Mexico | 3-7 days | Low (80) | Low (10%) | Automotive, Electronics |
| Vietnam | 2-3 weeks | Very Low (60) | Moderate (25%) | Apparel, Footwear, Electronics |
3. Carbon Transparency: Sustainability Becomes a Dealbreaker
Sustainability has gone from slogan to contract clause.
Sustainability is now a contractual requirement, with transparent carbon accounting becoming essential by 2025.
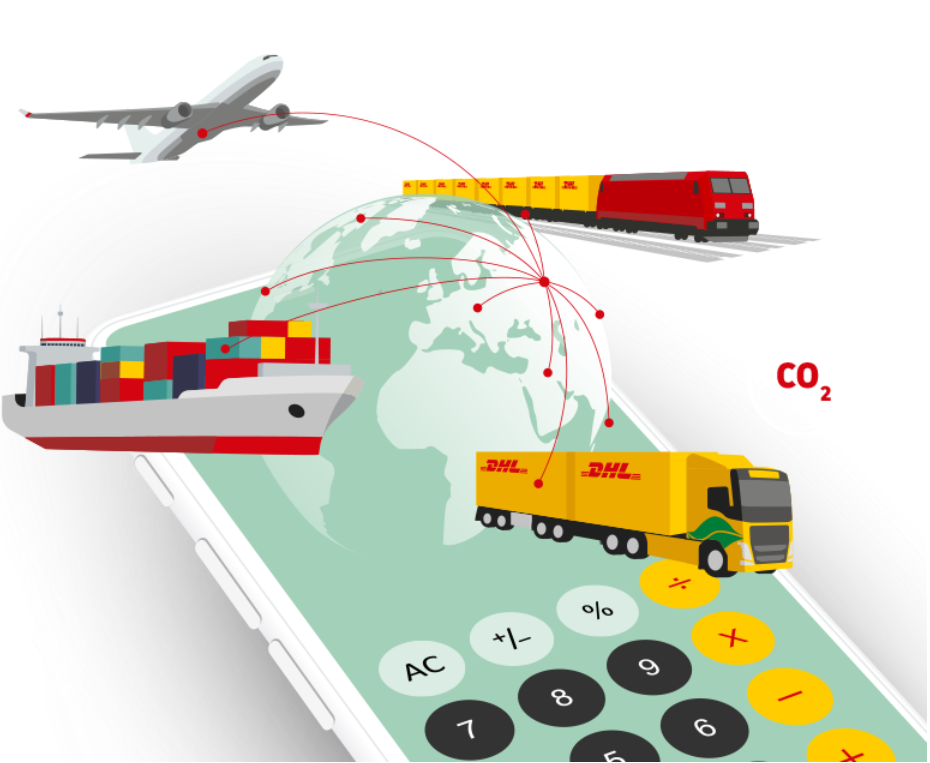

- Impact on Importers: Reporting Scope 3 emissions (including transportation) is critical, driven by regulations like the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) and corporate ESG mandates. EU importers face reporting requirements for emissions in goods like ceramics and chemicals. Logistics providers are responding with carbon dashboards and greener fuels like Bio-LNG and e-Methanol. China is investing heavily in green logistics, with EV fleets and renewable-powered warehouses.
- The Challenge/Opportunity: Demonstrating environmental responsibility ensures market access and boosts brand reputation. Adopt standards like the GLEC Framework to track emissions from freight.
| Metric | Requirement | Impact | Source/Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope 3 Emissions Reporting | Mandatory for EU CBAM (2026) | Ensures market access | EU Commission, 2024 |
| Carbon Reduction (Bio-LNG) | 30% emissions cut vs. diesel | Enhances brand reputation | Shell Sustainability Report, 2024 |
| EV Fleet Adoption (China) | 50% of logistics fleets by 2025 | Lowers final-mile emissions | BloombergNEF, 2024 |
| GLEC Framework Adoption | Standardized emissions tracking | 40% more accurate reporting | Smart Freight Centre, 2024 |
4. Digitized Ports and Smart Infrastructure: Smoothing the Flow
The port of the future is arriving faster than expected.
Port congestion and information gaps have long been pain points. The “smart port” concept is changing that.

- Impact on Importers: Technologies like blockchain-backed bills of lading, IoT sensors, and AI-assisted customs reviews are streamlining operations. IoT sensors cut spoilage rates for sensitive electronics by 20% by monitoring temperature in real time. Leading ports like Singapore, Rotterdam, and modernized Chinese ports are reducing delays and enhancing visibility.
- The Benefit: Faster clearance, reduced delays for time-sensitive shipments, and reliable transit data.
| Technology | Function | Impact | Source/Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blockchain Bills of Lading | Secure, tamper-proof documentation | 50% faster document processing | Maersk, 2025 |
| IoT Sensors | Real-time container monitoring | 20% lower spoilage for electronics | Seavantage, 2025 |
| AI Customs Reviews | Automated compliance checks | 40% reduction in clearance time | Prodensa, 2024 |
| Digital Port Integration | Unified data sharing | Fewer delays | ScienceDirect, 2024 |
5. E-Commerce Logistics: Evolving Beyond Raw Speed
E-commerce is maturing—and so are expectations.
The e-commerce boom continues, but customers now value reliability, seamless returns, and sustainability as much as speed.

- Impact on Importers (Cross-Border Focus): China dominates cross-border e-commerce with vast product selection and sophisticated logistics. For importers selling high-value goods online, managing customs, localized preferences, and returns is crucial. Regional hubs can reduce return costs for consumer electronics by 30% compared to shipping back to China. Strategies like micro-warehousing and low-emission final-mile delivery are becoming standard.
- Key Shifts: Growth in circular logistics for returns and refurbishment.
| Aspect | Customer Expectation | Solution | Impact | Source/Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delivery Speed | 3–5 days (cross-border) | Micro-warehousing | 30% faster delivery | Global Plugin, 2025, Freight Amigo, 2025 |
| Returns Management | Seamless, low-cost | Regional return hubs | 30% lower return costs | Dedola Estimate, 2025 | Low-Emission Delivery | Eco-friendly options | EV final-mile fleets | 25% emissions reduction | BloombergNEF, 2024 |
6. Labor Meets Automation: The Human-Tech Balance
Even the most advanced systems need humans—and 2025 is making that relationship more nuanced.
Warehouses are increasingly automated, but human expertise remains vital for high-value goods.
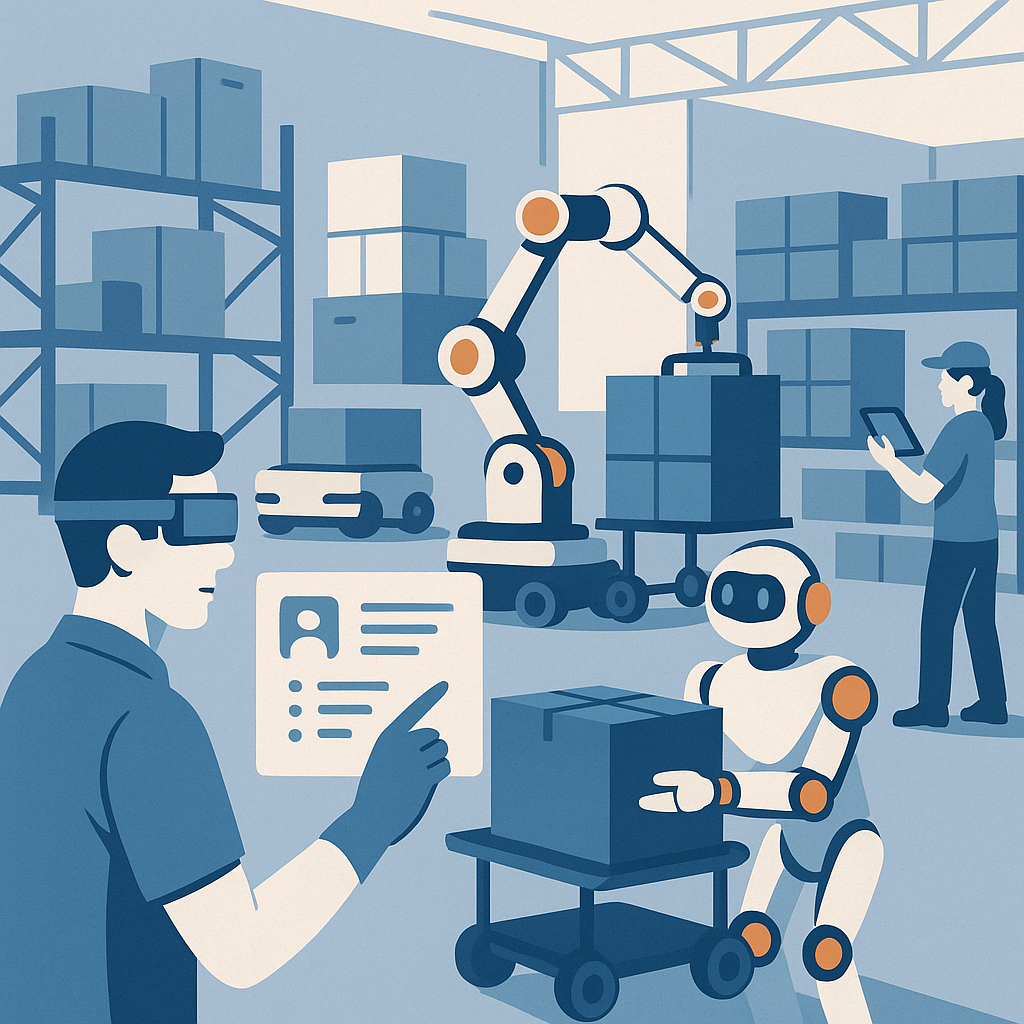

- Impact on Importers: Collaborative environments where technology supports skilled workers are the future. Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS) offers flexible automation during peak seasons, while Augmented Reality (AR) guides workers through complex tasks. China leads in warehouse automation but faces rising labor costs, driving tech adoption. Train staff in robotics maintenance or data analytics to keep pace with automated systems.
- The Goal: Balance technological efficiency with workforce upskilling to ensure productivity and quality handling.
| Aspect | Automation Benefit | Human Role | Impact | Source/Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Robotics-as-a-Service | Flexible peak-season capacity | Oversight and maintenance | 30% higher throughput | ABI Research, 2025 |
| AR-Guided Tasks | Error-free handling | Skilled execution | Fewer handling errors | Deloitte, 2025 |
| Data Analytics Training | Predictive insights | Decision-making | 20% better inventory accuracy | TadaNow, 2024 |
| Warehouse Automation (China) | High-speed sorting | Quality control for valuables | Faster processing | Logistics Business, 2024 |
7. Trade Policy & Geopolitics: Real-Time Logistics Impact
It’s no longer just about trucks and vessels—it’s about treaties, tariffs, and real-time policy shifts.
Logistics strategy is now tied to trade policy and geopolitical shifts, with tariffs and sanctions impacting costs.
- Impact on Importers (China & Beyond): U.S. tariffs on Chinese imports are highly volatile as of April 26, 2025. A White House announcement on April 8, 2025, increased duties on certain Chinese goods to 84%, with total effective rates averaging 145% when layered with existing tariffs, per CNBC (April 11, 2025). Some products face rates up to 245% due to reciprocal and fentanyl-related tariffs. China retaliated with 125% tariffs on U.S. goods. Monitor U.S. Customs Service bulletins or join trade groups like the NCBFAA for real-time updates.
- The Strategy: Agile compliance, scenario planning, supply chain mapping, and expert trade intelligence are essential. Our team recently saved a client 15% on duties by reclassifying auto parts.
| Tariff Type | Rate | Effective Date | Product Examples | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reciprocal Tariff | 125% | April 9, 2025 | Electronics, Machinery | White House, April 8, 2025 |
| Fentanyl Tariff | 20% | March 4, 2025 | General Goods | CBP, March 7, 2025 |
| Total Effective Rate | ~145% (avg.) | April 26, 2025 | Varies by product | CNBC, April 11, 2025 |
| Maximum Combined Rate | Up to 245% | April 26, 2025 | Specific high-tariff goods | NYT, April 12, 2025 |
Conclusion: Adaptation Isn’t Just a Trait, It’s Your Strategy
The logistics world of 2025 demands anticipation and adaptation. For small-to-midsize importers of high-value goods, thriving means embracing technology, building resilient supply chains, prioritizing sustainability, and staying informed on trade policies.
Choosing the right logistics partner is critical. Dedola Global Logistics combines cutting-edge technology with personalized service to navigate these trends. We focus on your specific needs, providing transparent data and proactive supply chain management for optimal performance.
2025 is well underway—is your supply chain keeping up?
Schedule a complimentary review with Dedola at www.dedola.com to uncover cost-saving opportunities, reduce delays, and gain clearer visibility into your shipments. Let’s put our expertise to work for your business.
Footnotes
- Nearshoring: A business strategy involving shifting manufacturing or sourcing operations closer to main end markets to reduce transportation costs and delivery times.
- Friendshoring: An international supply chain strategy where companies locate production and sourcing primarily in countries considered political and economic allies, prioritizing stability in trade relations.
- Scope 3 Emissions: Indirect greenhouse gas emissions occurring in a company’s value chain, including those from transportation and distribution (upstream and downstream), business travel, employee commuting, and waste generated from operations.
- Bio-LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas): A sustainable fuel derived from processing biological waste materials (like agricultural or food waste) via anaerobic digestion or gasification, creating a renewable form of LNG.
- e-Methanol: A synthetic liquid fuel produced by combining green hydrogen (H₂, derived from water electrolysis using renewable electricity) with captured carbon dioxide (CO₂).
- Blockchain Bill of Lading: A digital version of the traditional bill of lading document, using blockchain technology to securely record and transfer title and information about goods received for shipment, aiming to replicate the functions of its paper equivalent.
- IoT (Internet of Things) in Ports/Logistics: The integration of connected devices (like sensors, GPS trackers, RFID tags) into the logistics ecosystem, allowing autonomous data exchange to monitor cargo conditions (temperature, humidity), track location, and optimize operations.
- Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS): A business model where robotic solutions are accessed via subscription or pay-per-use, allowing companies to leverage advanced automation (e.g., in warehouses) without large upfront capital investment, providing scalability.
- Augmented Reality (AR) in Warehousing: Technology, typically delivered via smart glasses or wearable devices, that overlays digital information (like picking locations, instructions, or schematics) onto a worker’s real-world view, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in tasks like order picking or maintenance.
- Large Language Model (LLM): A type of artificial intelligence (AI) trained on vast amounts of text data to understand, process, generate, summarize, and translate human language effectively.
- Supply Chain Control Tower: A centralized hub, often powered by software and AI, that provides end-to-end visibility across a supply chain, integrating data from various systems (ERP, warehouse management, transport) to enable real-time monitoring, decision-making, and proactive exception management.
Disclaimer: Information regarding future tariffs and trade policies is based on publicly available analyses and reports as of late April 2025 and is subject to change. Consult with logistics and trade experts for the latest developments.



